This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Convolution implementation pages (Spring 2008 studies group under Ole Caprani)
Our goal is to implement a realtime plugin to do convolution.
The basic “Input Side” is way too slow (convolution implemented with two for loops), so we will be experimenting with a dft-multiply-idft algorithm (sometimes called “The Overlap-and-Save algorithm”) instead.
To do the actual fft we will use the fftw3 library (http://www.fftw.org), which implements the “Fastest Fourier Transform in the West” algorithm.
The next step is to implement at test the “Partitioned Overlap-and-Save” algorithm, where the filter is split into partitions prior to convolution.
Group
- Jonas Suhr Christensen - suhr@daimi.au.dk - 20032491
- Bent Bisballe Nyeng - deva@daimi.au.dk - 20001467
Analysis
The following graphs show the execution time of a single convolution iteration, using the overlap and save algorithm with various optimizations enabled.
The timings are produced using a Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU E6750 @ 2.66GHz, with 4096KB cache.
The algorithm optimizations are named as follows:
- Double This is an implementation with no particular optimizations.
- Float This is a simple implementation using float as the internal datatype.
- Real Double This is an implementation using real ffts instead of complex.
- Real Float This is an implementation using real ffts instead of complex, with float as internal datatype.
- MT Double This is an implementation running on multiple CPUs.
- MT Float This is an implementation with float as internal datatype, running on multiple CPUs.
- MT Real Double This is an implementation using real ffts instead of complex, running on multiple CPUs.
- MT Real Float This is an implementation using real ffts instead of complex, with float as internal datatype, running on multiple CPUs.
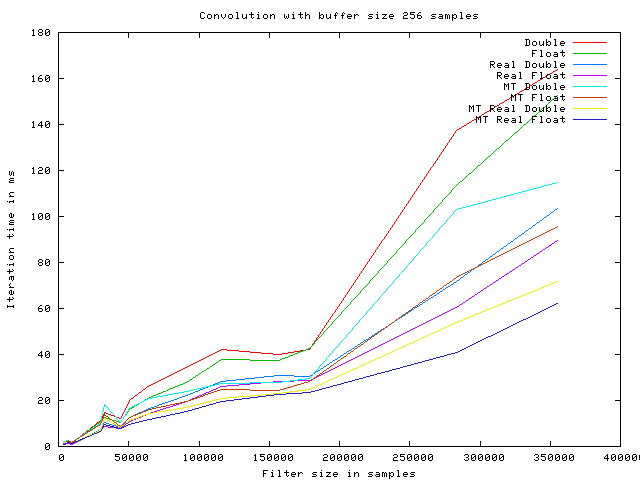
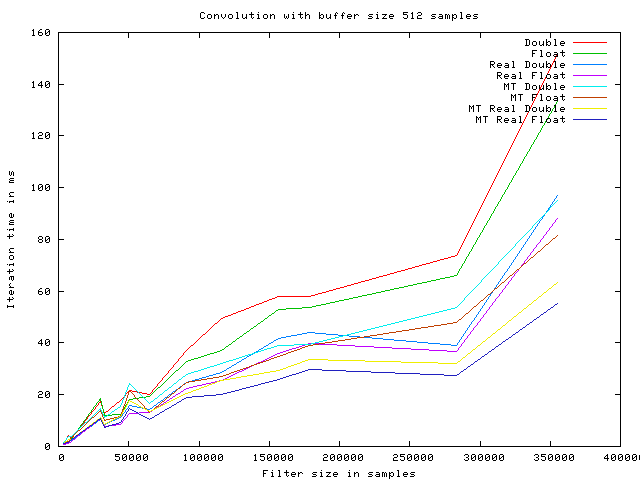
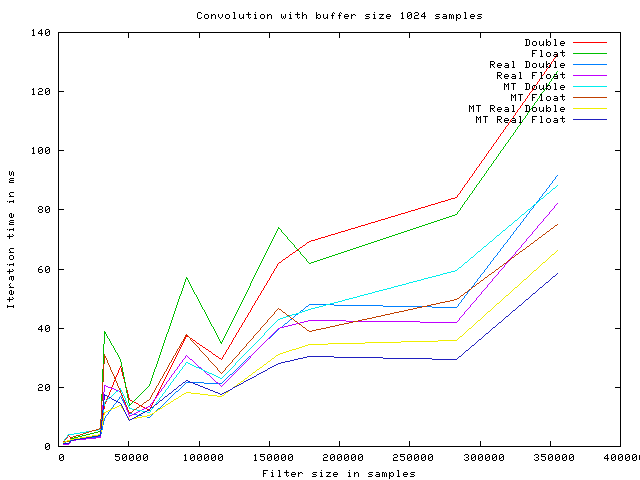
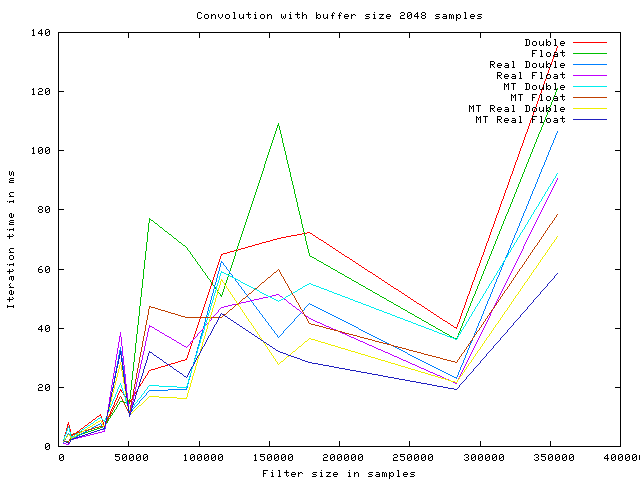
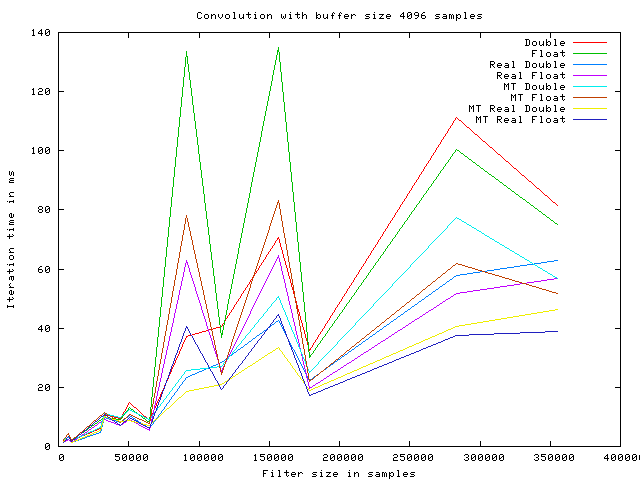
As it is seen on the graphs the speed improves with the buffer size increasing, up to 1024 samples. At this point the iteration time starts fluctuating. This may be caused by internal cache size on the given CPU.
Links
- http://www.fftw.org - The fftw library.
- http://archive.cnmat.berkeley.edu/~adrian/Csigproc.html - Some C optimizations that can be used when programming DSP.
- http://sunsite.univie.ac.at/Linux-soundapp/dsp.html - A list of links to various sites about audio and DSP programming.
- http://www.dspguide.com - A very good online book about audio convolution.
- http://people.scs.fsu.edu/~burkardt/c_src/fftw3/fftw3.html - Some info about the fftw3 library.
- http://www.ludd.luth.se/~torger/brutefir.html#bruteconv_3 - Some info about partitioned convolution.
- http://www.aurora-plugins.it/Public/Papers/164-Mohonk2001.PDF - More on partitioned convolution.
- http://www.linuxdevcenter.com/lpt/a/586 - A LADSPA tutorial
Code
Compile with:
g++ -O2 -mmmx -msse -msse2 conv_opt.cc -o conv_opt -lfftw3 -lsndfile
or
g++ -O2 -mmmx -msse -msse2 conv_opt.cc -o conv_opt -DFFTW_FLOAT -lfftw3f -lsndfile
to use floating point fftw instead of double.
The actual code is shown below:
#include <stdlib.h> #include <fftw3.h> #include <sndfile.hh> #include <string.h> #include <assert.h> #include "sys/timeb.h" //#define BUFFER_SIZE_MS 113 //ms 113, // Find a size with small prime factors #define BUFFER_SIZE_MS 1000 //ms 113, // Find a size with small prime factors #define SAMPLE_RATE_HZ 44100 //hz #define BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES 4096 //(SAMPLE_RATE_HZ * BUFFER_SIZE_MS / 1000) //#define MEASURE #ifdef FFTW_FLOAT #define FFTW_DATATYPE fftwf_complex #define FFTW_PLAN_DFT fftwf_plan_dft_1d #define FFTW_EXECUTE fftwf_execute #define FFTW_PLAN fftwf_plan #define FFTW_DESTROY_PLAN fftwf_destroy_plan #define FFTW_FREE fftwf_free #define FFTW_MALLOC fftwf_malloc typedef float sample_t; #else #define FFTW_DATATYPE fftw_complex #define FFTW_PLAN_DFT fftw_plan_dft_1d #define FFTW_EXECUTE fftw_execute #define FFTW_PLAN fftw_plan #define FFTW_DESTROY_PLAN fftw_destroy_plan #define FFTW_FREE fftw_free #define FFTW_MALLOC fftw_malloc typedef double sample_t; #endif typedef struct { sample_t *data; size_t size; } samples_t; samples_t *new_samples(sample_t *data, size_t size) { samples_t *samples = (samples_t*)malloc(sizeof(samples_t)); samples->data = data; samples->size = size; return samples; } samples_t *read_data(const char *filename, double scale) { printf("Loading %s ... ", filename); fflush(stdout); SndfileHandle sfh(filename); size_t size = sfh.seek(0, SEEK_END); sfh.seek(0, SEEK_SET); // size_t size = 3; sample_t *data = (sample_t*)malloc(sizeof(sample_t) * size); sfh.read(data, size); printf("[%d samples] ... ", size); fflush(stdout); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { data[i] = scale * data[i]; } // for(int i = size / 2; i < (size / 2) +20; i++) printf("\t[%d] %f\n", i, data[i]); samples_t *samples = new_samples(data, size); printf("done\n"); return samples; } void write_data(const char *filename, samples_t *samples) { printf("Saving %s ...", filename); fflush(stdout); // for(int i = samples->size / 2; i < (samples->size / 2) +20; i++)printf("\t[%d] %f\n", i, samples->data[i]); SndfileHandle sfh(filename, SFM_WRITE, SF_FORMAT_WAV | SF_FORMAT_PCM_16, 1, 44100); sfh.write(samples->data, samples->size); printf("done\n"); } #define RE 0 #define IM 1 static FFTW_DATATYPE *hfft = NULL; static FFTW_DATATYPE *outm = NULL; static FFTW_DATATYPE *out = NULL; static FFTW_DATATYPE *inx = NULL; static FFTW_DATATYPE *xfft = NULL; void init_fftw(samples_t *h) { FFTW_PLAN p; int size = BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES + h->size - 1; hfft = (FFTW_DATATYPE*) FFTW_MALLOC(sizeof(FFTW_DATATYPE) * size); FFTW_DATATYPE *inh = (FFTW_DATATYPE*) FFTW_MALLOC(sizeof(FFTW_DATATYPE) * size); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { inh[i][RE] = inh[i][IM] = 0; } for(int i = 0; i < h->size; i++) { inh[i][RE] = h->data[i]; } p = FFTW_PLAN_DFT(size, inh, hfft, FFTW_FORWARD, FFTW_ESTIMATE); FFTW_EXECUTE(p); FFTW_DESTROY_PLAN(p); FFTW_FREE(inh); outm = (FFTW_DATATYPE*) FFTW_MALLOC(sizeof(FFTW_DATATYPE) * size); out = (FFTW_DATATYPE*) FFTW_MALLOC(sizeof(FFTW_DATATYPE) * size); inx = (FFTW_DATATYPE*) FFTW_MALLOC(sizeof(FFTW_DATATYPE) * size); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { inx[i][RE] = inx[i][IM] = 0; } xfft = (FFTW_DATATYPE*) FFTW_MALLOC(sizeof(FFTW_DATATYPE) * size); } void deinit_fftw() { FFTW_FREE(hfft); FFTW_FREE(out); FFTW_FREE(outm); FFTW_FREE(inx); FFTW_FREE(xfft); } #ifdef MEASURE long static time_used; #endif samples_t *conv_fftwc_preprocess(samples_t *x, size_t hsize/*samples_t *h*/) { assert(hfft); // init_fftw not called! assert(out); // init_fftw not called! assert(outm); // init_fftw not called! assert(inx); // init_fftw not called! assert(xfft); // init_fftw not called! #ifdef MEASURE struct timeb systime; long begin = 0; long end = 0; ftime(&systime); begin = systime.time * 1000 + systime.millitm; #endif FFTW_PLAN p; int size = x->size + hsize - 1; sample_t *data = (sample_t*)calloc(sizeof(sample_t), size); samples_t *y = new_samples(data, size); for(int i = 0; i < x->size; i++) { inx[i][RE] = x->data[i]; } p = FFTW_PLAN_DFT(size, inx, xfft, FFTW_FORWARD, FFTW_ESTIMATE); FFTW_EXECUTE(p); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++ ) { outm[i][RE] = hfft[i][RE] * xfft[i][RE] - hfft[i][IM] * xfft[i][IM]; outm[i][IM] = xfft[i][IM] * hfft[i][RE] + xfft[i][RE] * hfft[i][IM]; } p = FFTW_PLAN_DFT(size, outm, out, FFTW_BACKWARD, FFTW_ESTIMATE); FFTW_EXECUTE(p); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { data[i] = out[i][RE] / size; } FFTW_DESTROY_PLAN(p); #ifdef MEASURE ftime(&systime); end = systime.time * 1000 + systime.millitm; printf("\t Time consumed: %d\n", end - begin); time_used = end - begin; #endif return y; } sample_t *filter(const sample_t *input, size_t filter_size) { unsigned int buffer_size = BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES + filter_size - 1; static sample_t *buffer = (sample_t*)calloc(buffer_size, sizeof(sample_t)); static unsigned int p = 0; samples_t *input_s = new_samples((sample_t *)input, BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES); samples_t *y; y = conv_fftwc_preprocess(input_s, filter_size); for(int i = 0; i < BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES; i++) { buffer[(i + p + filter_size - 1) % buffer_size] = 0; //y->data[i]; } for(int i = 0/* BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES*/; i < buffer_size; i++) { buffer[(i + p) % buffer_size] += y->data[i]; } // alloker returbuffer sample_t *output_buffer = (sample_t*)malloc(BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES * sizeof(sample_t)); // kopier retsultat til output buffer for(int i = 0; i < BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES; i++) { output_buffer[i] = buffer[(i + p) % buffer_size]; } p += BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES; // frigør y free(input_s); return output_buffer; } sample_t puls = 0.5; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { // y(n)=\sum_{k=-\infty}^\infty h(k)x(n-k) if(argc != 4) { printf("Usage %s [filterfile] [soundfile] [outputfile]\n", argv[0]); exit(1); } int xsz, hsz; const char *filterfile = argv[1]; const char *inputfile = argv[2]; const char *outputfile = argv[3]; samples_t *h = read_data(filterfile, 0.08); // samples_t *h = new_samples(&puls, 0.5); samples_t *x = read_data(inputfile, 0.5); // samples_t *x = new_samples(&puls, 1); size_t s = h->size + x->size - 1; sample_t *d = (sample_t*)malloc(s * sizeof(sample_t)); samples_t *y = new_samples(d, s); // 0 padding sample_t *pd = (sample_t*)malloc((y->size) * sizeof(sample_t)); for(int i = 0; i < x->size; i++) { pd[i] = x->data[i]; } for(int i = x->size; i < y->size + (y->size % BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES); i++) { pd[i] = 0; } x = new_samples(pd, x->size); init_fftw(h); int e = 0; #ifdef MEASURE // find a good delta value (ie. small prime factors) int o = 20000; for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { printf("Measuring %d: ", i); filter(&(x->data[0]), h->size - i); if(time_used < o) { e = i; o = time_used; } } #endif for(int i = 0; i < y->size; i += BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES) { #ifdef MEASURE printf("[c:%d, s:%d](%d, %d)", i, y->size, BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES, e); fflush(stdout); #endif sample_t *data = filter(&(x->data[i]), h->size /*- e*/); for(int j = 0; j < BUFFER_SIZE_SAMPLES; j++) { y->data[j + i] = data[j]; } free(data); } deinit_fftw(); write_data(outputfile, y); free(y); free(h); free(x); }